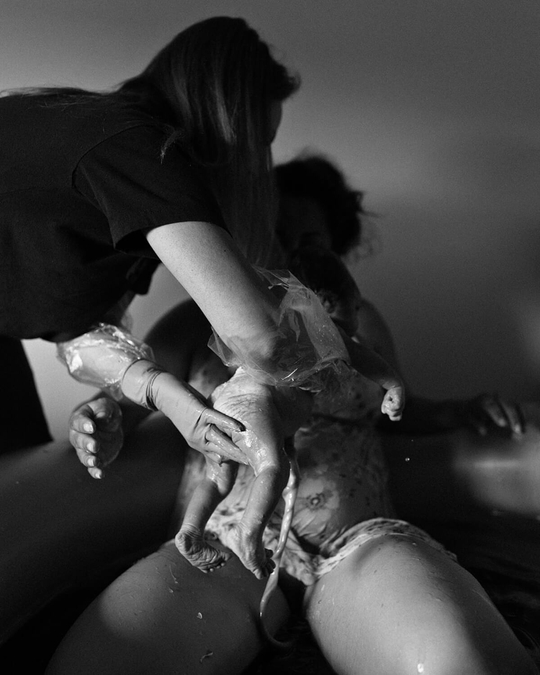
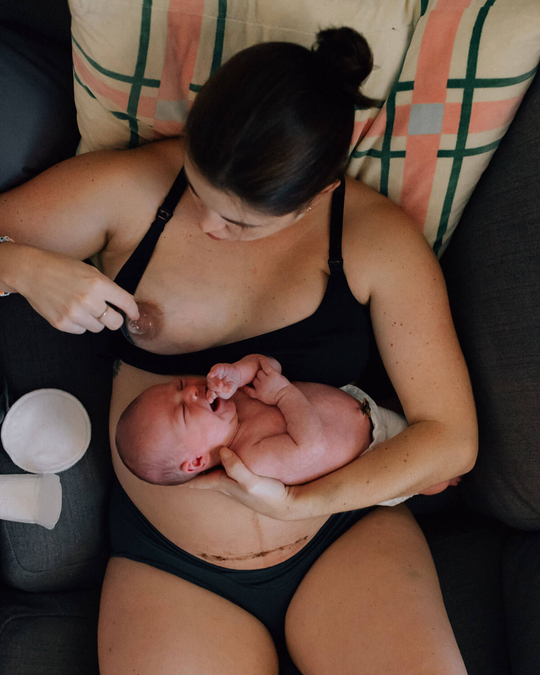
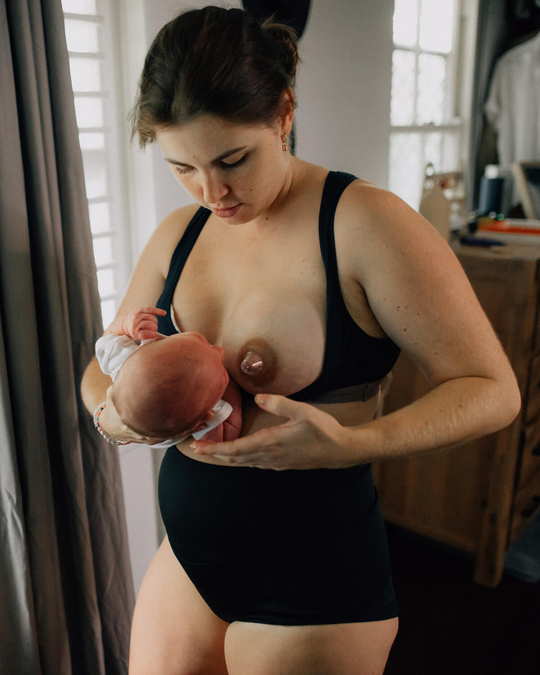
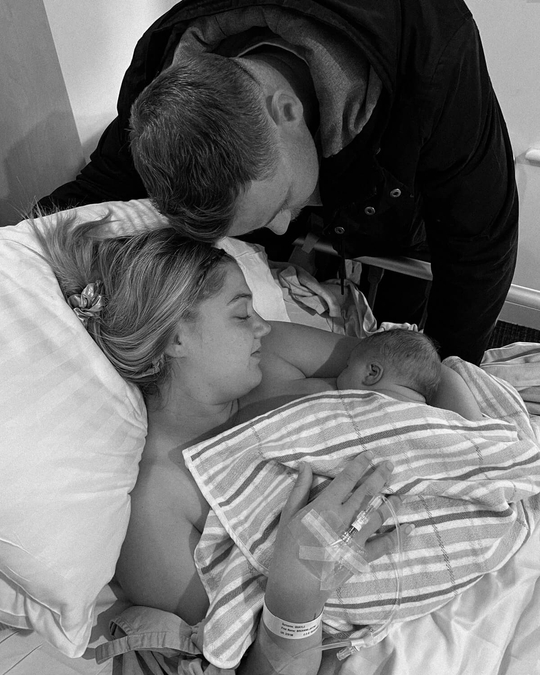
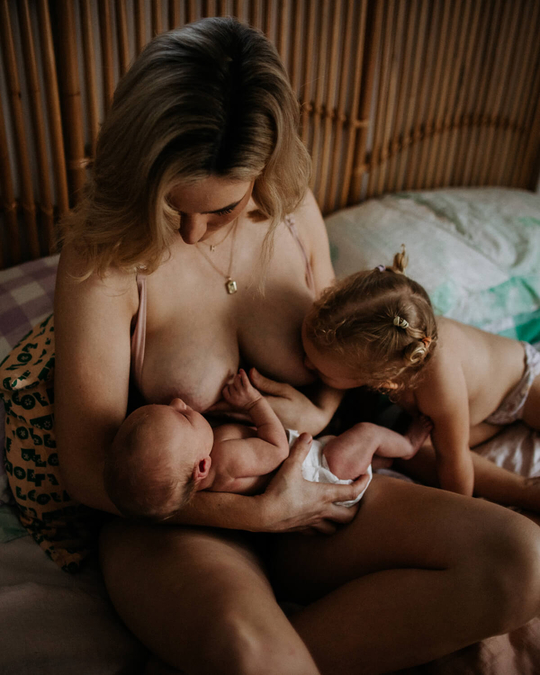
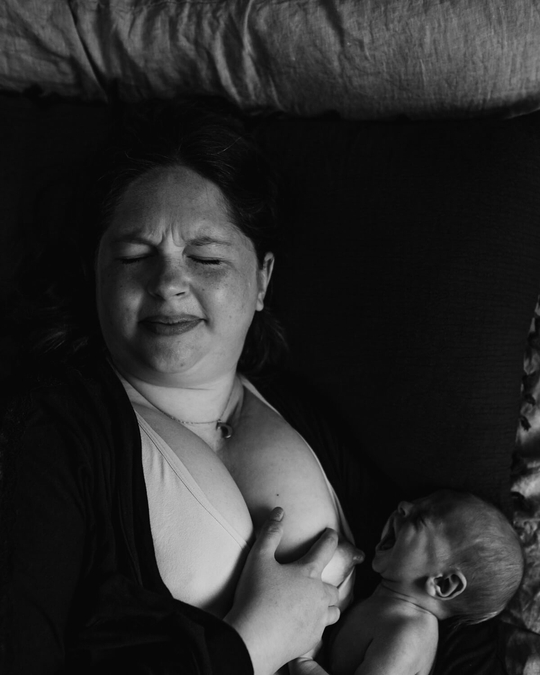
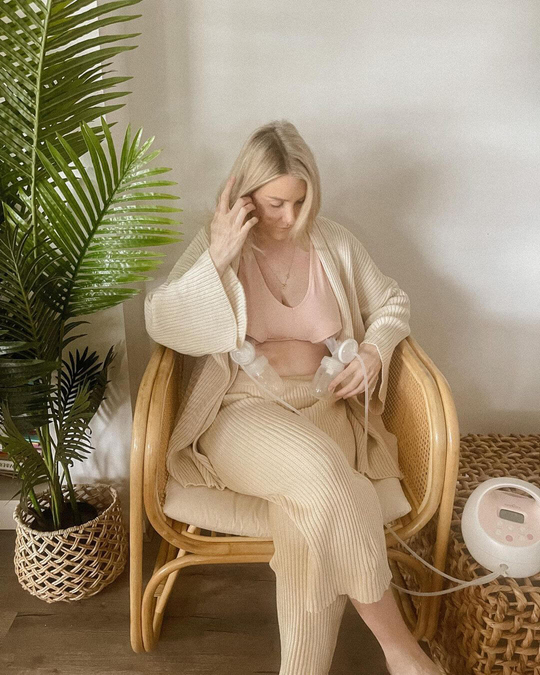
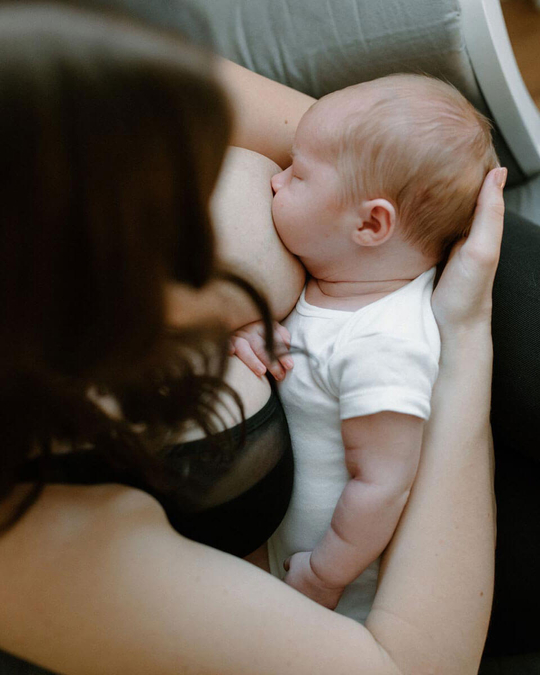
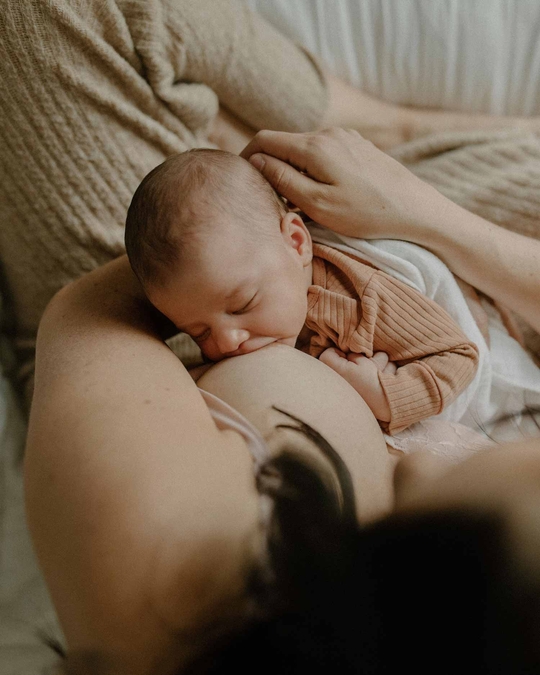
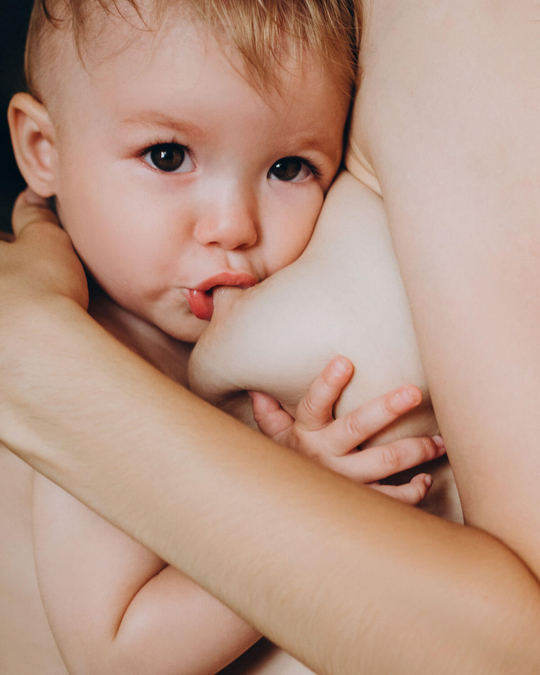
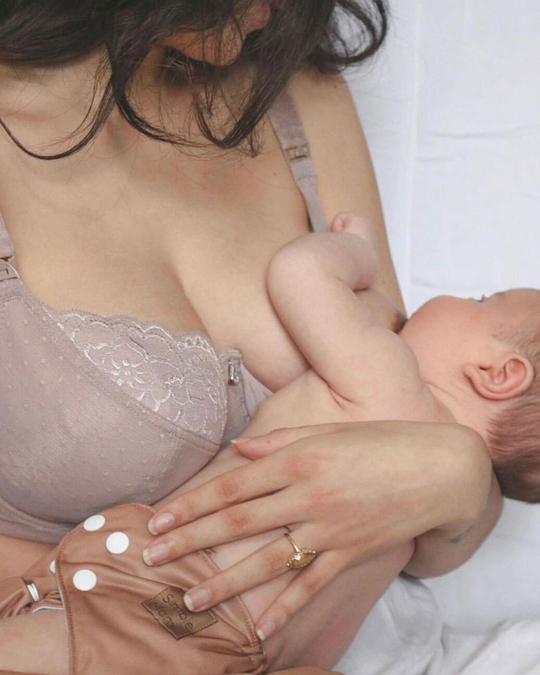
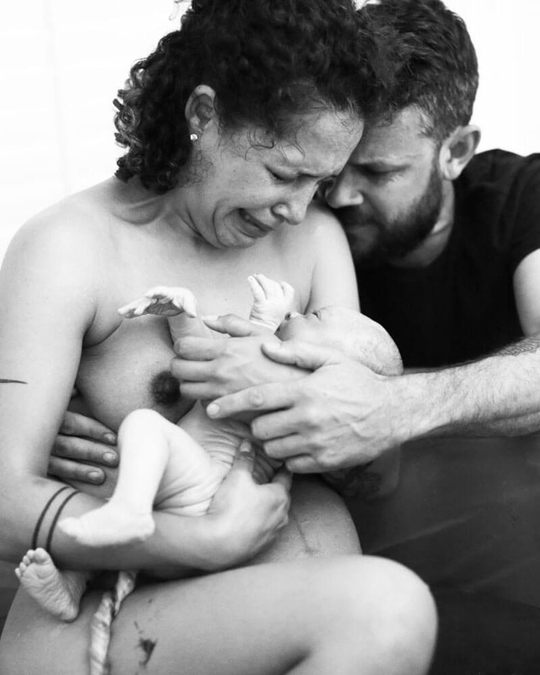
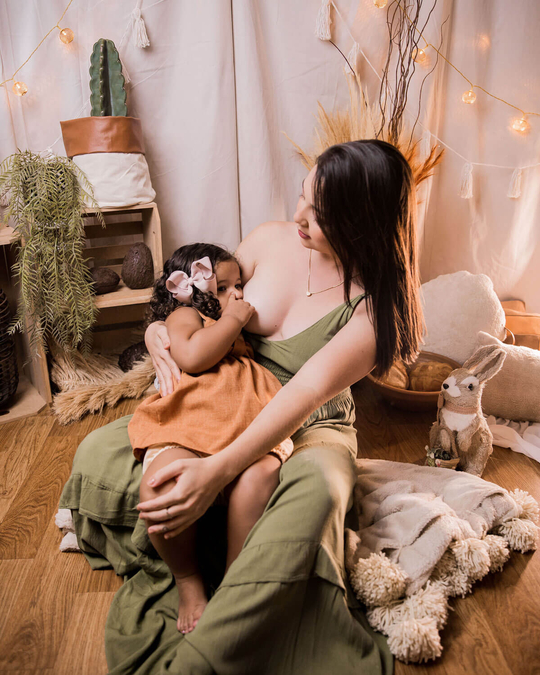
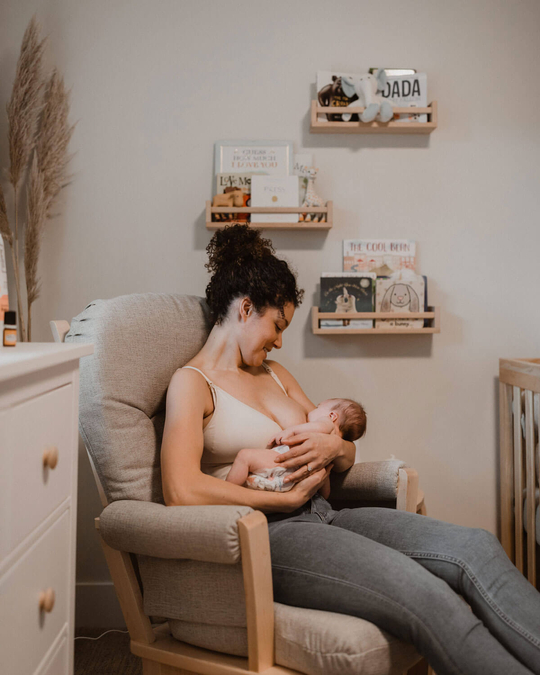
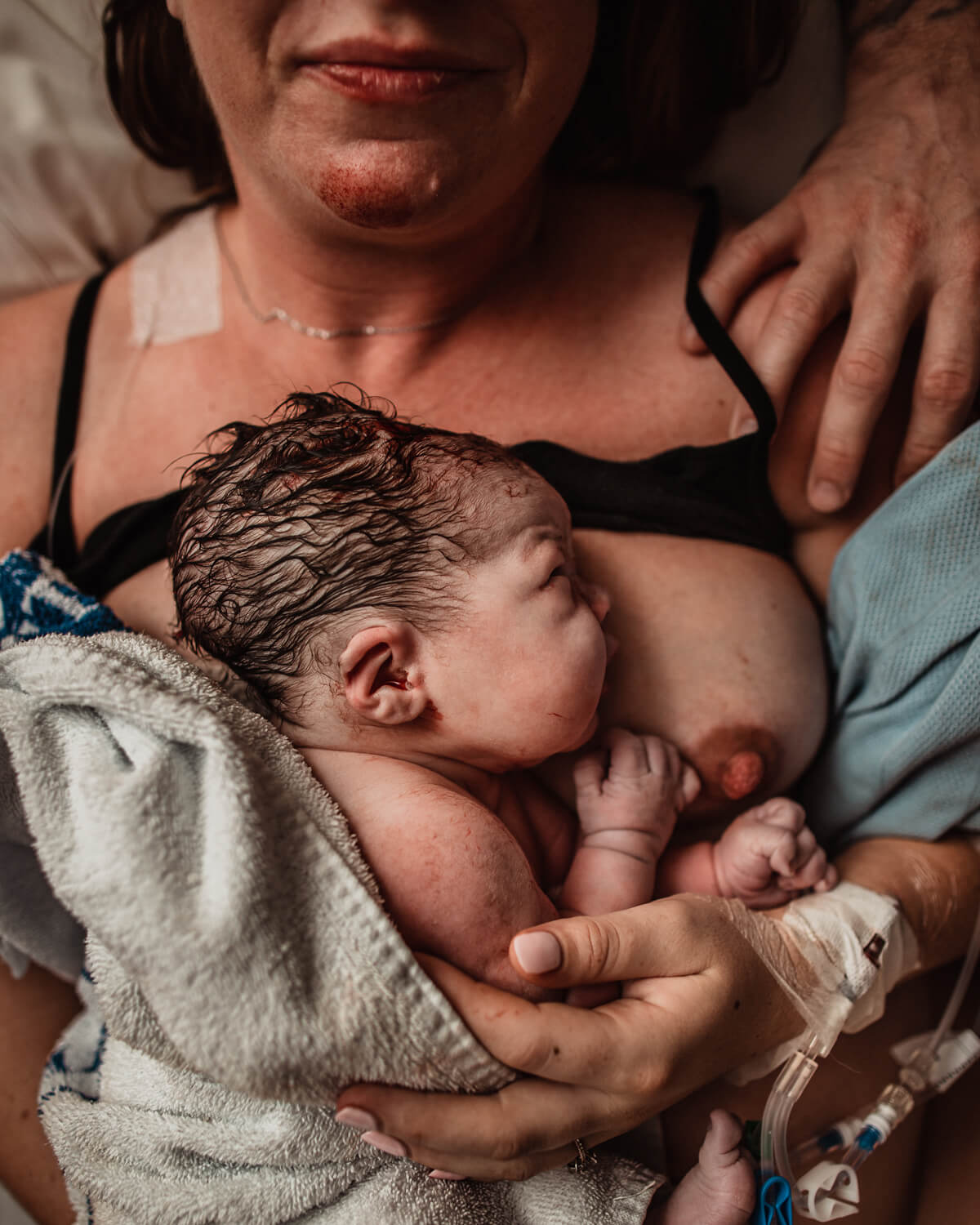
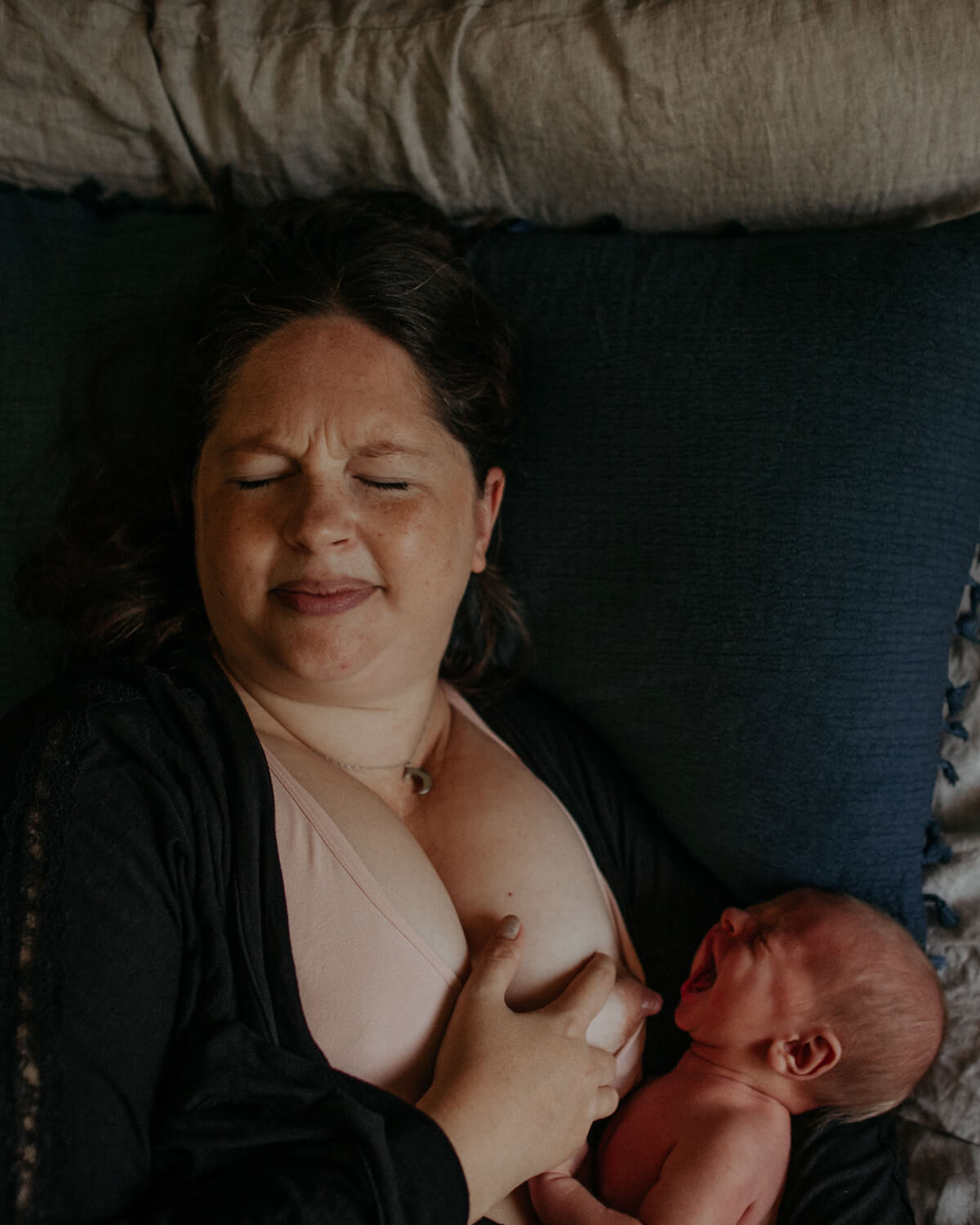
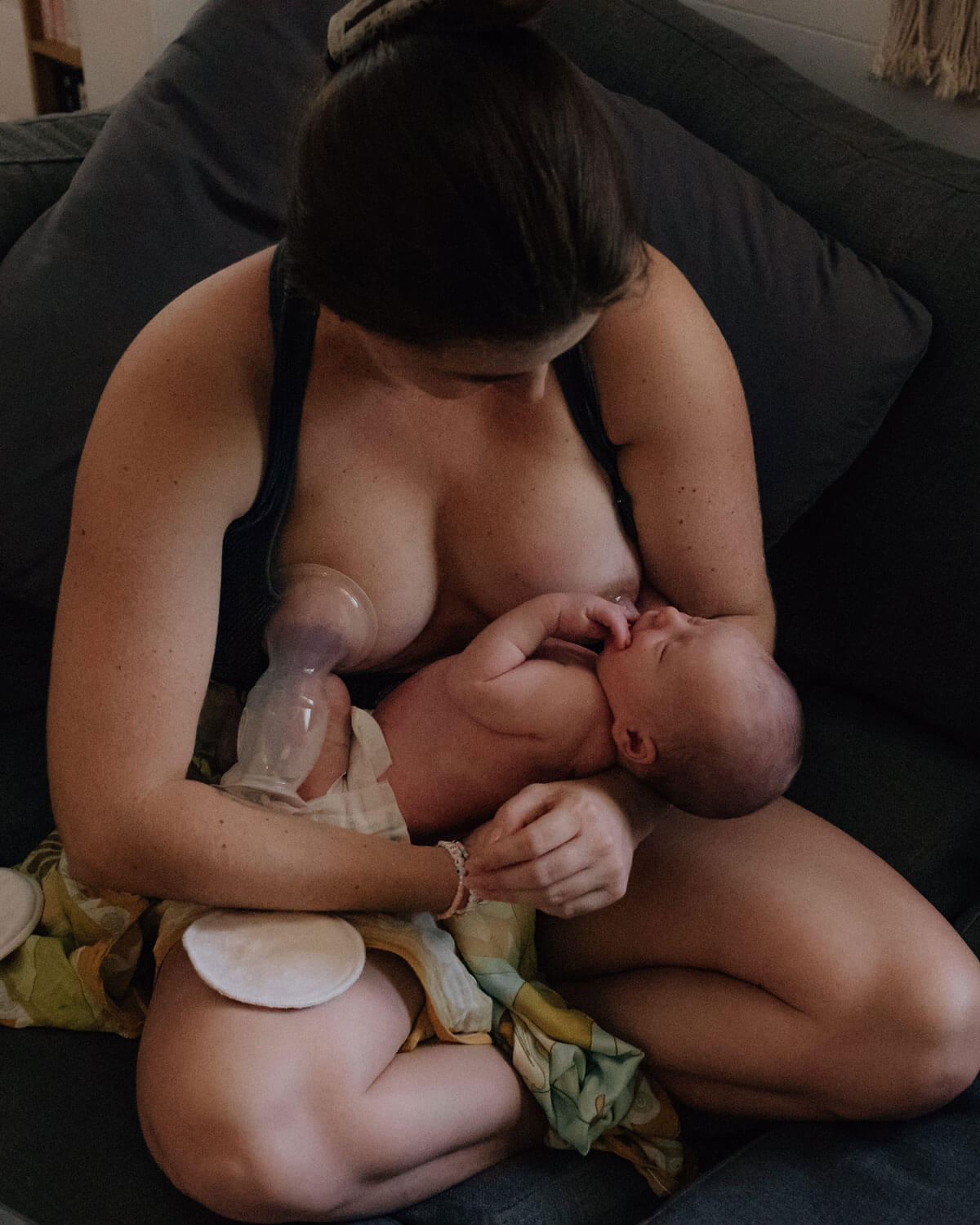
Breastfeeding, like most things, has its own language. Understanding commonly used terminology will help guide you through your research, and is the key to a successful breastfeeding journey. Read on for Cake’s ‘Breastfeeding for Pacifiers’ Glossary.
We have compiled a list of breastfeeding terms and their definitions to get you started.
Areola: The areola is the dark, round area that surrounds your nipple.
Alveoli: The small cluster of cells or glands that produce and secrete milk.
Blocked milk ducts: When the milk ducts become clogged or blocked and milk is unable to flow freely. This condition may lead to mastitis if left unresolved.
Biological nursing: A laid back breastfeeding position. This is particularly useful for women with smaller breasts and for women who want to catch up on some rest while breastfeeding.
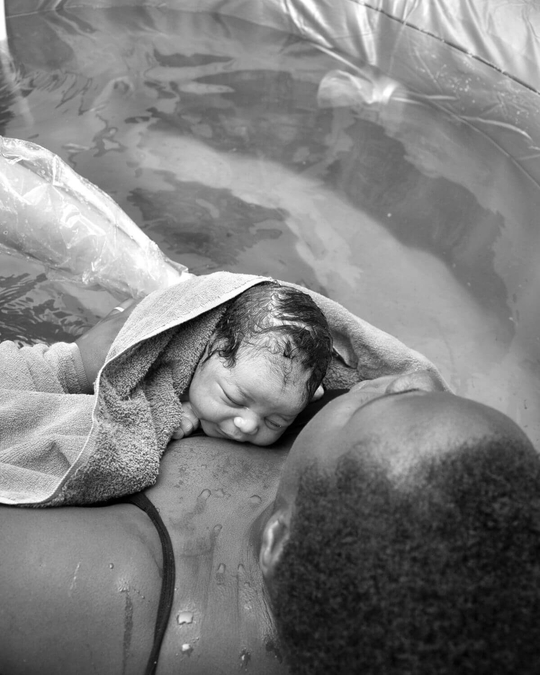
Breast crawl: When a newborn is placed on her mother’s abdomen soon after birth, they all have the ability to crawl on their own and to decide themselves to take the first breastfeed.
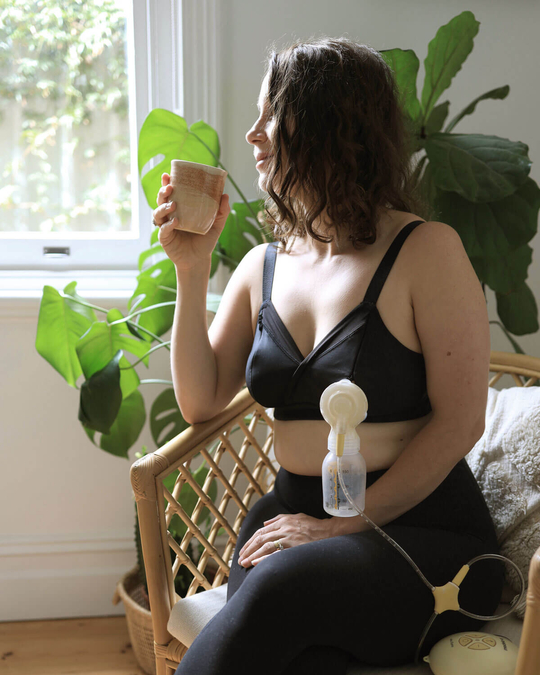
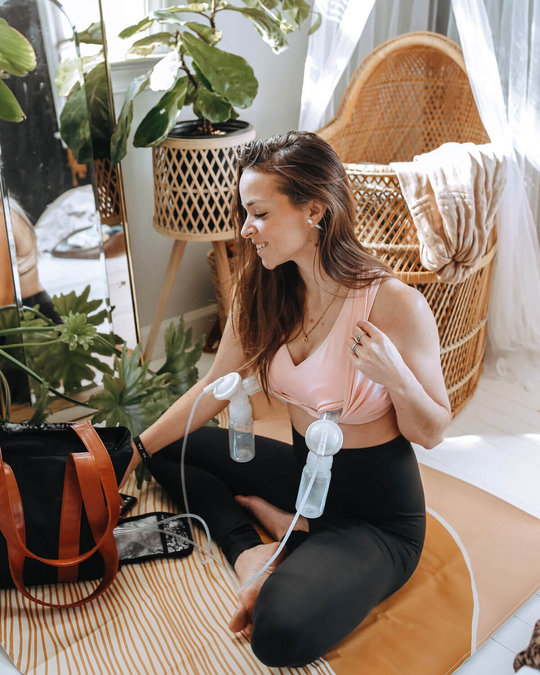
Breast pump: A specially designed machine that draws breast milk from the breast using suction. Can be a manual hand pump or electric.
Cabbage leaf: When used as a compress on your breast, it may reduce swelling as cabbage leaves contain superior anti-inflammatory compounds when applied to engorged breasts. They also feel nice and cool.
Colostrum: A thick, creamy, yellow substance that is produced by the breast post birth and for the first 3 or so days after the baby is born. This is the baby’s first feed/s and is full of valuable nutrients and immune boosting enzymes designed to give the baby the best start in life.
Cooper’s ligaments: The ligaments that support the breast tissue. These must be supported during breastfeeding to inhibit stretching out as non-retracting ligaments may lead to sagging.
Cluster feeding: When your baby wants a lot of food in a short amount of time. Usually occurs prior to a growth spurt.
Clutch hold: Also known as the football hold. This is a breastfeeding position used by women who have had C-sections, twins or have large breasts. Baby is simply tucked under the arm, much like a football, and is fed this way.
Cradle hold: This is probably the most common breastfeeding position adopted by women. The baby lies across your body, resting into your elbow. Your other arm slides under the baby supporting their back.
Colic: A common condition that affects 1 in 5 babies in the early months. Baby experiences abdominal pain, which causes an erratic sleep and crying pattern.
Duct: A passageway that stores and carries milk from the alveoli to the nipple for consumption.
Engorgement: When the breast becomes sore and swollen. This is a result of the breasts being too full of milk.
Expressed breast milk: When you pump or hand express to produce breast milk.
Extended breastfeeding: When a toddler continues to breastfeed past the age of 1 year.
Feeding on demand: Baby is fed when they are hungry. Feeding is not timed to a clock, but to your baby’s appetite.
Flat nipple: When the nipple does not protrude. This may make it more difficult to breastfeed for some.
Flange: The part of the apparatus that connects to your breast from your breast pump.
Flanged lips: When your baby’s lips are extended, open and slightly curled forming an oval shape. Sign of a good latch is flanged lips.
Foremilk: This is the first milk released by the breast at the beginning of every feed. This milk is much more watery and will quench baby’s thirst.
Formula: Chemically derived and synthesised cow or plant based milk with added fats and nutrients, which is dehydrated to form a powder. When mixed with water it mimics breast milk. This is for mothers who are unable, or choose not to, breastfeed their baby.
Frenulum: The membrane or piece of tissue in your mouth that joins the upper lip to your gums. Also the piece that joins your tongue to the inner edge of your jaw.
Full night’s sleep: Unexplained phenomena.

Galactagogues: Foods, herbs and medicines that may increase your milk supply. Some of these include whole grains such as oats, broccoli, chickpeas and fennel.
Hind milk: This is the milk the breast produces during the middle of the feed. It is much thicker and richer and contains the beneficial nutrients and fats that baby needs to develop and grow.
Inverted nipple: The nipple retracts into itself. Breastfeeding may be more difficult.
Immunity: Protection against infection.
Inflammation: An infected area of redness, warmth and swelling. It will often feel painful. You should consult your healthcare provider, as medication may be required.
IBCLC: International Board Certified Lactation Consultants.
Kangaroo care: When babies are placed skin to skin. A technique often adopted for premature babies. It has been proven to help stimulate feeding, produce oxytocin and a sense of security.
Lactation: The secretion of milk.
Lactation consultant: Trained professionals who specialise in breastfeeding support.
La Leche League: A breastfeeding organisation that provides women with support.
Lactose: The sugar found in milk.
Lanolin: A healing cream used on cracked nipples. Not suitable for vegans.
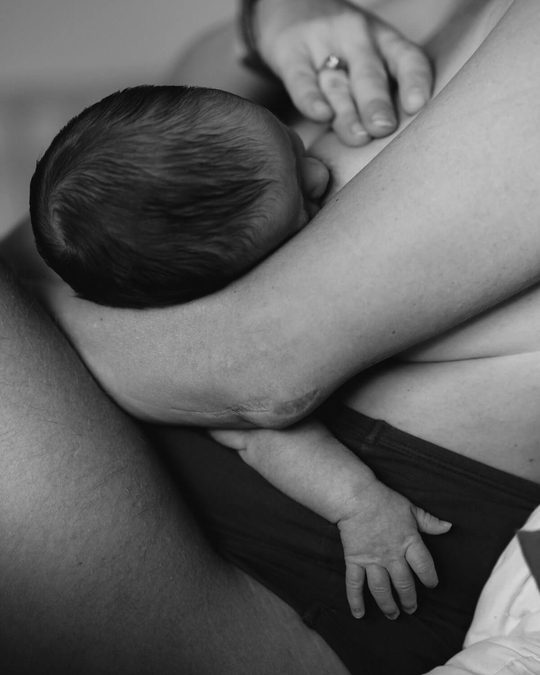
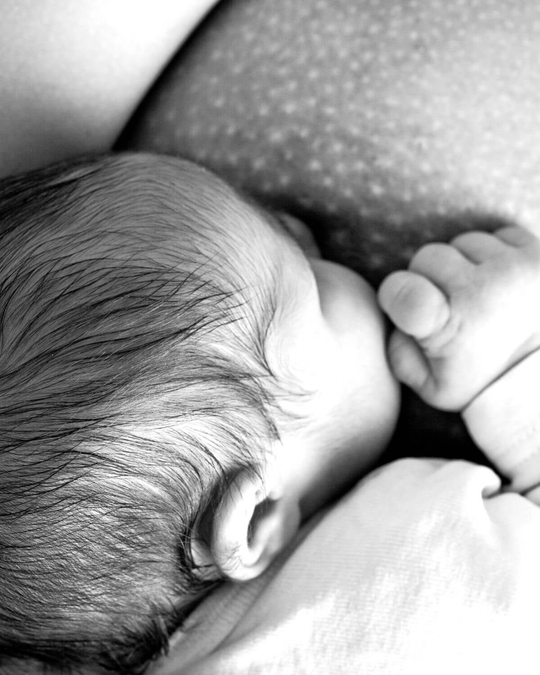
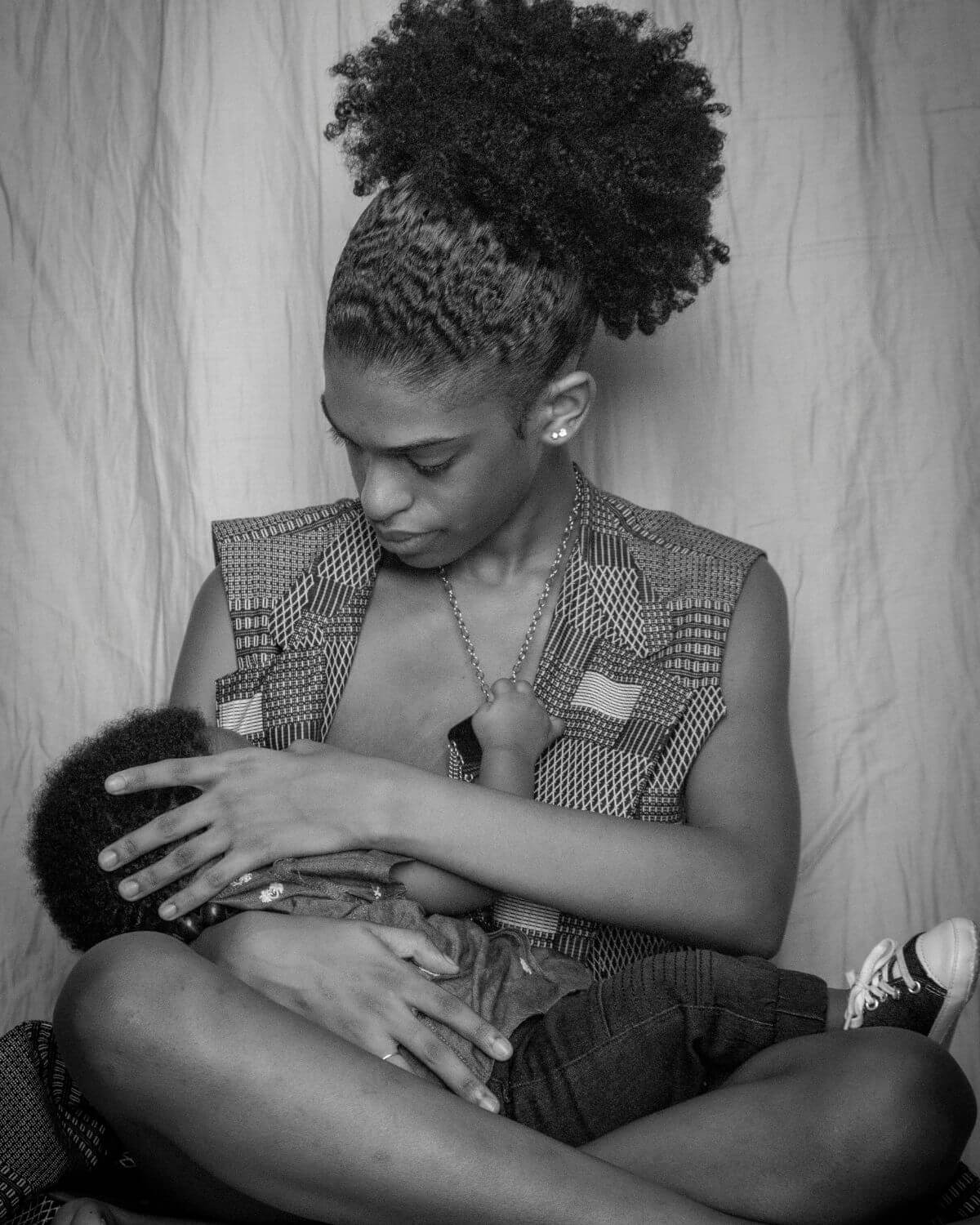
Latch: The attachment of your baby’s mouth to your breast in order to feed. A good latch is a good seal around the baby’s mouth.
Leakage: When lactating breasts leak breast milk from the nipple. This tends to happen when the breast is very full (close to feeding time), the breasts are pressed into or the nursing bra is too tight.
Let down: This is the initial sensation felt when the milk is released from the breast. Sometimes you can feel it (occasionally it may be painful) and sometimes you can’t.
Let down pains: The pain that occurs when you are having a let down. These can feel like pins and needles to a burning/aching sensation in your breasts.
Lipase: The enzyme that breaks down the fat in breast milk.
Lip tie: When the piece of tissue behind your baby’s upper lip (frenulum) is too thick or stiff, they can inhibit the upper lip from moving freely. This is called a lip tie.
Liquid gold: Often referred to as colostrum as it is gold in colour and is the first feeds for your baby before your milk comes in.
Nursing bra: A specially designed bra that enables a woman to breastfeed discreetly with the aid of drop down cups.
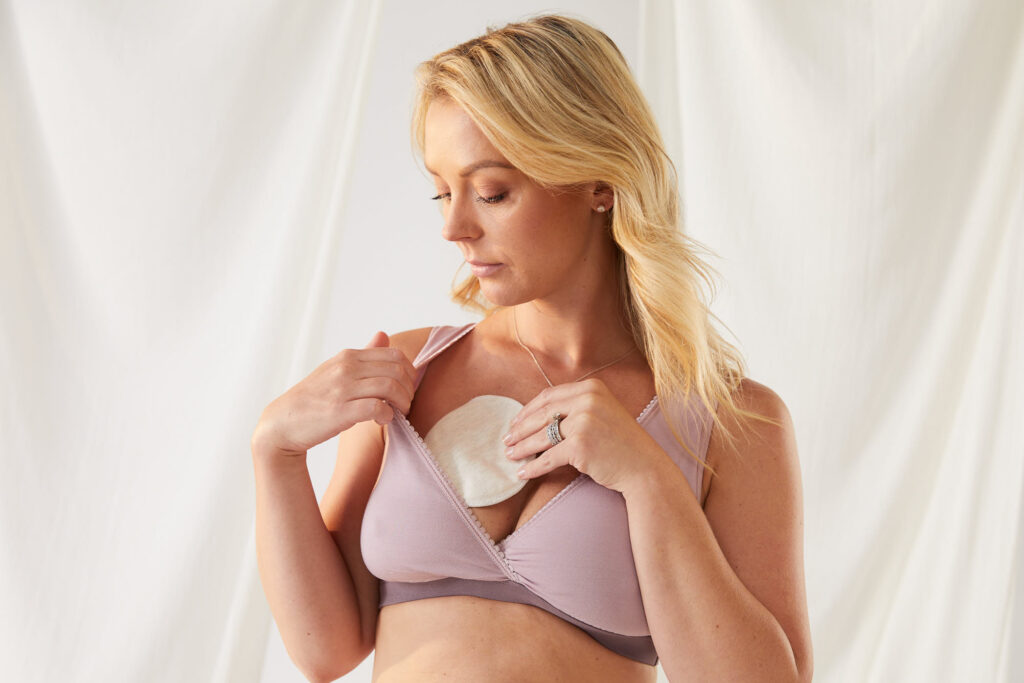

Nursing pads: Absorbent pads designed to draw moisture away from lactating breasts.
Nutrition: Taking in healthy food to help aid in growth and development.
Nipple: Protrudes from the areola and releases breast milk through multiple ducts (holes).
Nipple shield: A protective plastic cup used to shield the nipple when the baby breastfeeds. Some women use it to aid in protecting the nipple against damage caused by breastfeeding in the early weeks.
Nursing pillow: A specially designed pillow used to support a baby while breastfeeding.
Night feed: Feeding baby during the night.
Mastitis: A painful infection in the breast caused by blocked milk ducts. A woman can become very unwell and suffer from flu-like symptoms and should seek medical assistance.
Milk blister: It’s when a blocked duct appears close to the skin on your nipple and cells form over the top of it making a bubble or a blister.
Montgomery glands: Pimple-like in appearance bumps that are found on the areola. They produce oils that lubricate the nipple. Sometimes these appear for the first time when pregnant.
Overactive let down: This is the milk gushing effect that occurs when you haven’t fed your baby for a while or are just starting a feed or pumping session.
Oxytocin: A hormone that is released from your brain when you breastfeed. Oxytocin is also known as the ‘love’ or ‘feel good’ hormone. Other activities that release oxytocin are dog-patting, baths, exercise and hugs.
Plugged ducts (blocked ducts): A plugged duct is when the blockage is at the nipple and the milk forms a plug.
Pumping: Breast milk is drawn from the breast via a breast pump and can be stored for later use in the fridge or freezer.
Prolactin: A hormone produced by the pituitary gland that is responsible for milk production.
Reflux: When a baby spits up what they have just swallowed. Not to be confused with vomiting.
Reverse cycling: This is when a baby feeds more at night than it does during the day.
Rooting: The instinctive turn of the head and nuzzling as the baby looks for the breast/nipple to feed.
Sleep feeding: Feeding the baby while they are still sleeping. The position that is usually used for this is either side or hovering over the top of them so they don’t have to wake up.
Spray: When milk sprays out of your breast. This occurs when your breast is uncovered and you are pre-feed, mid-feed or stimulated.
Tandem breastfeeding: When a mother breastfeeds two children at once.
Thrush: A yeast infection. This can occur where moisture is trapped and unable to dry/air properly. This can occur in the baby’s mouth and spread to the mother’s nipple and vice versa.
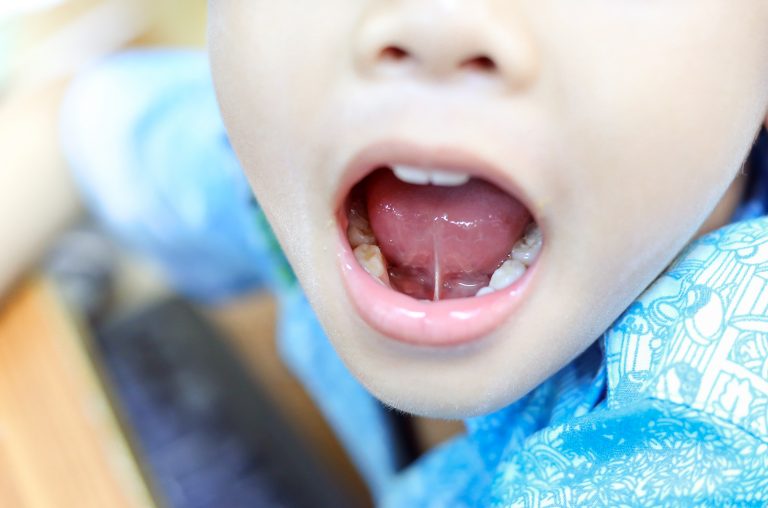
Tongue tie: A condition where the tissue connecting the baby’s tongue to the floor of the mouth is short and tight. This can restrict a baby’s breastfeeding ability as they may not be able to properly latch.
LIKE WHAT YOU READ?
Join CakeMama Club & get 10% OFF your first order!
Plus you’ll get tips + tricks for pregnancy, postpartum & breastfeeding, get member-only offers, earn CakeCoins every time you shop + more. Learn more